Explain storage mechanism in HBase and Column-Oriented Database &, Row-Oriented Database.
STORAGE MECHANISM IN HBASE
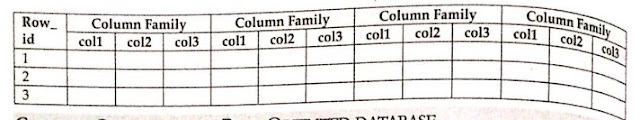
HBase is a column-oriented database, with tables ordered by row. Only column families, which are key-value pairs, are defined in the table structure. A table contains many columns families, each of which can include any number of columns. Subsequent column values are saved on the disk in a logical order. A timestamp is associated with each cell value in the table.
In a nutshell, in an HBase:
- The table is a collection of rows.
- The row is a collection of column families.
- A Column family is a collection of columns.
- The column is a collection of key-value pairs.
An example schema of a table in HBase is provided below.
COLUMN-ORIENTED AND ROW-ORIENTED DATABASE
Column-oriented databases, as opposed to row-oriented databases, store data tables as portions of columns of data. They will have column families.
Row-Oriented Database
- It is suitable for the Online Transaction Process(OLTP).
- Such databases are designed for a small number of rows and columns.
Column-Oriented Database
- It is suitable for Online Analytical Processing (OLAP).
- Column-oriented databases are designed for huge tables.




Comments
Post a Comment