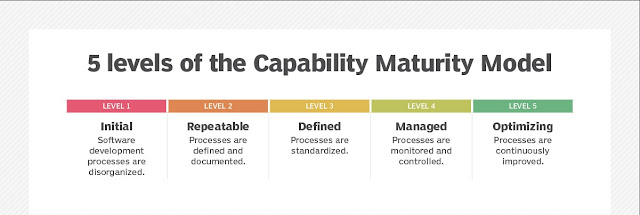
Suppose of you have purchased 500 pieces of pants for Rs 800 per piece . You would then sell the pants to a store for Rs 1000 per piece, Rs 1500 is incurred as a transportation cost. Calculate ROI.
No. of pants=500 the cost price of 1 pant= Rs 800 The cost price of 500 pants = Rs 800*500 = 400000 Transportation cost = Rs 1500 Total investment = CP + Transportation cost = 400000 + 1500 = Rs 401500 S.P of 1 pant = Rs 1000 S.P of 500 pant = Rs 1000*500 = Rs 500000 Profit = S.P - Total investment = 500000 - 401500 = Rs 98500 Now, ROI =( Profit/Total investment ) *100% = (98500/401500)*100% = 24.53%